labuladong如何判断回文链表
234. 回文链表
方法1:链表转列表,双指针逼近
将链表转化为列表,然后利用左右双指针技巧,从两端到中间逼近
# Definition for singly-linked list.
# class ListNode(object):
# def __init__(self, x):
# self.val = x
# self.next = None
class Solution(object):
def isPalindrome(self, head):
"""
:type head: ListNode
:rtype: bool
"""
# 转成列表
stack=[]
while head:
stack.append(head.val)
head=head.next
# 左右双指针逼近
l=0
r=len(stack)-1
while l<=r:
if stack[l]!=stack[r]:
return False
else:
l+=1
r-=1
return True方法2:反转后半部分链表后,逐个比较节点值
思路
- 边界条件(如[] 或者 [2])直接返回
- 快慢指针找中点
- 反转以slow为开头的链表
- 只需判断p2存在时,p1的前半部分元素是否与p2一样
步骤
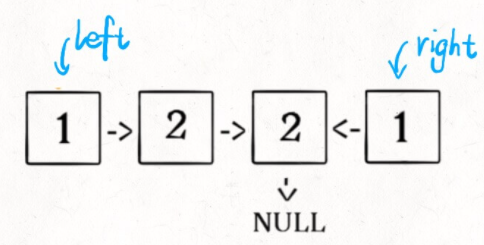
以偶数为例(奇数类似)
链表:1->2->2->1
下标:[0] [1] [2] [3]
- 快慢指针后,slow指向第二个2(下标为[2]),fast已跳出链表
- 此时slow后面的链表为
2->1。反转时,2(下标为[2])指向prev的None,1指向2。最后有None<-2<-1(此时prev在下标[3]处)。(注意:此时前半段中,下标为[1]的节点2仍然指向下标为[2]的节点2) - 此时,以head开头的p1为
1->2->2->None,以prev开头的p2为None<-2<-1,所以只需判断p2存在时,p1是否等于p2。
# Definition for singly-linked list.
# class ListNode(object):
# def __init__(self, x):
# self.val = x
# self.next = None
class Solution(object):
def isPalindrome(self, head):
"""
:type head: ListNode
:rtype: bool
"""
# 边界条件,直接跳出,如[] 或者 [2]
# if not head or not head.next: return True
if not (head and head.next): return True # 必须有括号,and后取其反
# 快慢指针找中点
slow=head
fast=head
while fast and fast.next:
slow=slow.next
fast=fast.next.next
# 反转以slow开始的后半部分链表
prev = None
cur=slow
while cur:
cur.next,prev,cur=prev,cur,cur.next
p1=head
p2=prev
# 只需判断p2存在时,p1是否等于p2
while p2:
if p1.val!=p2.val:
return False
p1=p1.next
p2=p2.next
return True
- 完整示例:输出链表操作的结果
#########开始:构建链表及链表基本操作########### # 节点类 # Definition for singly-linked list. class Node: def __init__(self, val=0, next=None): self.val = val self.next = next # 链表类:用于存放节点 class LinkedList(object): def __init__(self): self.head = None # 判断链表是否为空 def isEmpty(self): return self.head == None # 给链表添加节点 def add(self, val): newNode=Node(val) # 构建一个新的节点,该节点的值为val # 头结点存在,把cur指向头结点,cur逐步跳到链表尾部,然后添加节点 if (self.head): cur=self.head while (cur.next): cur = cur.next cur.next=newNode # 通过next,在尾部不断连接节点 else: # 这是一个空链表,则在头结点处添加该节点 self.head=newNode # 判断链表的长度 def size(self): count=0 cur=self.head while(cur): count+=1 cur=cur.next print(count) # 搜索某个元素是否存在 def search(self,item): cur=self.head while(cur): if cur.val==item: return True else: cur=cur.next return False # 打印该链表 def printLL(self): cur=self.head while(cur): print(cur.val) cur=cur.next #########结束:构建链表及链表基本操作########### class Solution: def isPalindrome(self, head: Node) -> bool: if not head or not head.next: return True slow=head fast=head while fast and fast.next: slow=slow.next fast=fast.next.next pre=None cur=slow while(cur): cur.next, pre, cur = pre, cur, cur.next # cur.next=pre # pre=cur # cur=cur.next slow.next=None while(pre): if pre.val!=head.val: return False pre=pre.next head=head.next return True if __name__ == '__main__': # 构建链表对象 l=LinkedList() l.add(1) l.add(2) l.add(2) l.add(1) # 构建Solution对象 s=Solution() print(s.isPalindrome(l.head)) # 输出True或者False
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
bool isPalindrome(ListNode *head) {
// 边界条件:只有0或1个节点
if (head == nullptr || head->next == nullptr){
return true;
}
// 找链表中点
ListNode *slow = head;
ListNode *fast = head;
while (fast != nullptr && fast->next != nullptr){
slow = slow->next;
fast=fast->next->next;
}
// 反转以slow为开头的后半段链表
ListNode * pre=nullptr;
ListNode * cur=slow;
while(cur!=nullptr){
ListNode* tmp=cur->next;
cur->next=pre;
pre=cur;
cur=tmp;
}
// 当以pre为开头的链表存在时,判断该链表是否与原始链表重合
while (pre!=nullptr){
if (pre->val !=head->val){
return false;
}
pre=pre->next;
head=head->next;
}
return true;
}
};



