labuladong 递归反转链表的一部分
92. 反转链表 II
方法1.递归反转链表
(只是说明递归方法的思想,本题优解应参考方法2)
- 先看例题206. 反转整个链表
- 对于递归算法,最重要的就是明确递归函数实现的功能
(而不是跳进递归中),因此,reverseList函数定义为:输入一个节点 head,将「以 head 为起点」的链表反转,并返回反转之后的头结点
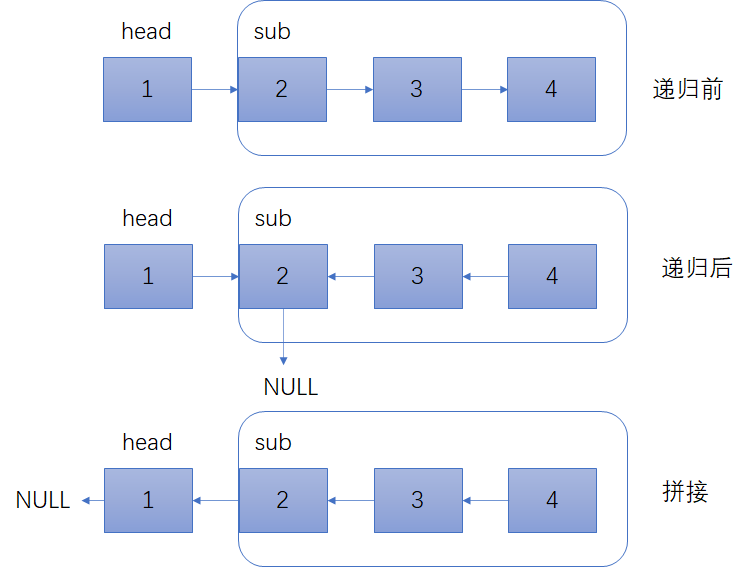
# Definition for singly-linked list. # class ListNode(object): # def __init__(self, x): # self.val = x # self.next = None class Solution(object): def reverseList(self, head): # 递归结束条件 if head==None or head.next==None: return head # reverseList函数返回反转后的头结点 last=self.reverseList(head.next) head.next.next=head head.next=None return last/** * Definition for singly-linked list. * struct ListNode { * int val; * ListNode *next; * ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {} * ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {} * ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {} * }; */ class Solution { public: ListNode* reverseList(ListNode* head) { if (head==nullptr || head->next==nullptr){ return head; } ListNode *sub=head->next; ListNode* tail=reverseList(sub); sub->next=head; head->next=nullptr; return tail; } };
- 先用递归实现:反转以head开头的前n个节点
- 首先,如果 m == 1(因为头结点是从1开始计数的),就相当于反转链表开头的 n 个元素,也就是函数
reverseN(head, n)(也是reverseBetween结束递归的条件) - 如果 m != 1 怎么办?如果我们把 head 的索引视为 1,那么我们是想从第 m 个元素开始反转;如果把 head.next 的索引视为 1 呢?那么相对于 head.next,反转的区间应该是从第 m - 1 个元素开始的;那么对于 head.next.next 呢……因此有:
# 如果不是第一个,那么以下一个为头结点开始递归,直到触发m==1递归终止条件 head.next = self.reverseBetween(head.next, m-1, n-1)
综上,反转m到n之间的节点的整体代码为:
def reverseBetween(self, head: ListNode, m: int, n: int) -> ListNode:
# 先用递归实现:反转以head开头的前n个节点
def reverseN(head, n):
if n == 1:
successor = head.next # 拿到后继节点
return head, successor
# 以 head.next 为起点,需要反转前 n - 1 个节点
last, successor = reverseN(head.next, n-1)
head.next.next = head
head.next = successor
return last, successor
if m == 1: # 递归终止条件
# 这里应该是反转以m为开头的n-m+1个节点,
# 所以应该写成res, _ = reverseN(head, n-m+1),只是m等于1,所以写成res, _ = reverseN(head, n)也可以
res, _ = reverseN(head, n)
return res
# 如果不是第一个,那么以下一个为头结点开始递归,直到触发条件
head.next = self.reverseBetween(head.next, m-1, n-1)
return head/**
* Definition for singly-linked list
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode *successor = nullptr;
ListNode *reverseN(ListNode *head, int t) {
if (t == 1) {
successor = head->next;
return head;
}
ListNode *last = reverseN(head->next, t - 1);
head->next->next = head;
head->next = successor;
return last;
}
ListNode *reverseBetween(ListNode *head, int m, int n) {
if (m == 1) {
ListNode *res = reverseN(head, n - m + 1);
return res;
}
head->next = reverseBetween(head->next, m - 1, n - 1);
return head;
}
};
方法2. 找到要翻转部分的链表,将其翻转,再与原链表拼接
- 复习一下逐个反转链表元素的代码:
- pre -> cur (pre在前,cur 在后)
- 把cur的next指向pre,然后pre和cur分别向右跳一格。(利用同步赋值语句同时实现这些功能)
- 同步赋值表达式首先将右侧的表达式按照顺序进行计算,然后再赋值给左侧的变量
class Solution(object): def reverseList(self,head): pre=None cur=head while cur: cur.next,pre,cur=pre,cur,cur.next return pre不合并的写法:
class Solution(object): def reverseList(self, head): """ :type head: ListNode :rtype: ListNode """ # 申请两个节点,pre和 cur,pre指向None pre = None cur = head # 遍历链表,while循环里面的内容其实可以写成一行 while cur: # 记录当前节点的下一个节点 tmp = cur.next # 然后将当前节点指向pre cur.next = pre # pre和cur节点都前进一位 pre = cur cur = tmp return pre
思路
- 先添加dummy节点,并连接在头结点前面
- cur跳到位置m处,pre在cur左面
- 反转m到n的节点
- 连接各节点
# class ListNode(object):
# def __init__(self):
# self.val=x
# self.next=None
class Solution(object):
def reverseBetween(self, head, m, n):
dummy=ListNode(-1)
dummy.next=head
pre=dummy
for _ in range(m-1):
pre=pre.next
cur=pre.next
node=pre
# node保存m的前一个节点,为后续连接做准备
# cur为反转的当前节点,node为cur的上一个节点
for _ in range(n-m+1): #反转m到n的节点
cur.next,node,cur=node,cur,cur.next #注意顺序,cur.next 在最前
#连接反转后的各节点
pre.next.next=cur
pre.next=node
return dummy.next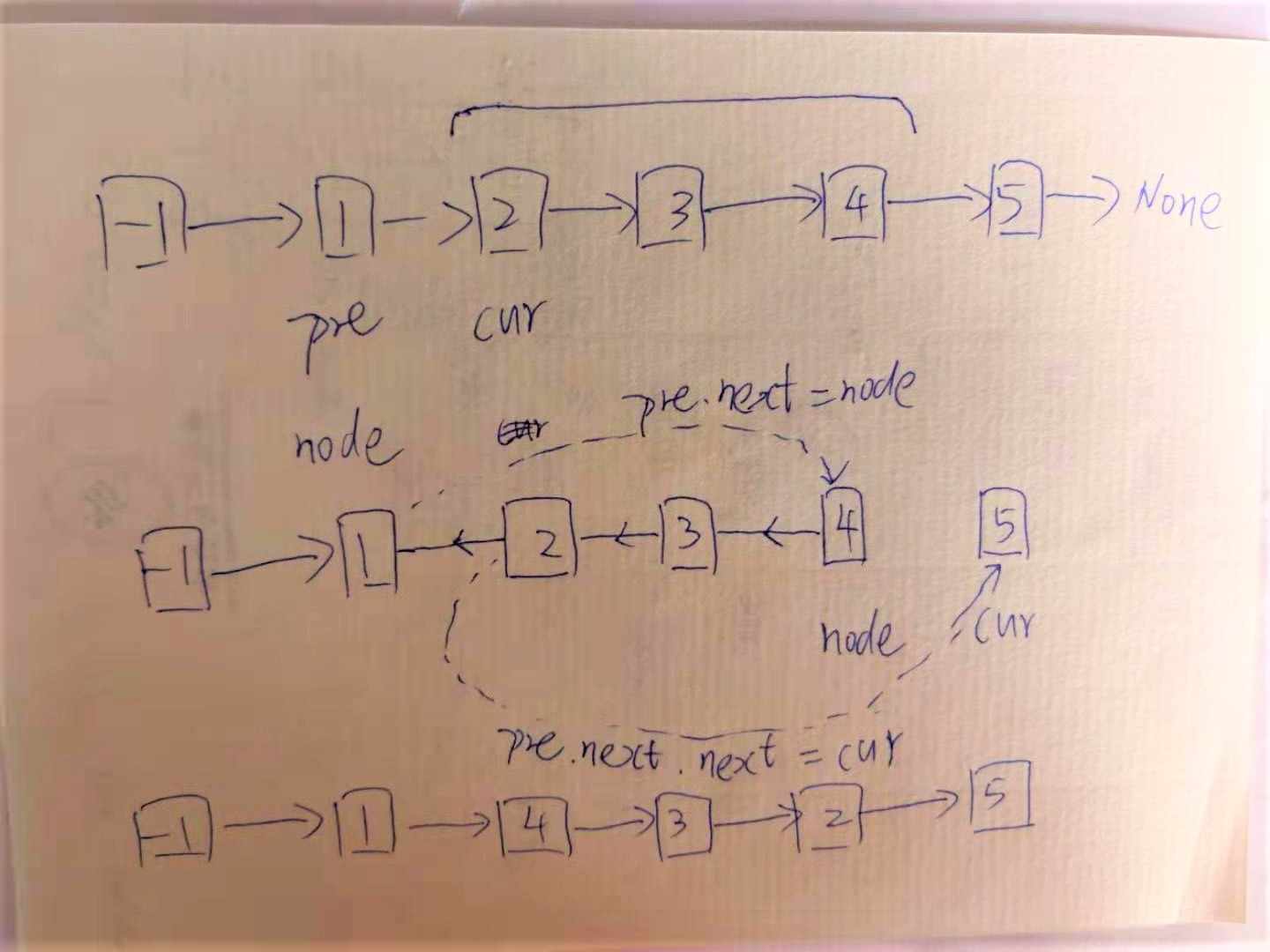
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* reverseBetween(ListNode* head, int m, int n) {
// m和n指向同一个节点
if(m == n) return head;
ListNode* dummy = new ListNode(-1);
// 把指针跳到需要反转的位置:pre为开始反转的前一个节点,cur为开始反转的节点
dummy->next=head;
ListNode* pre=dummy;
for (int i = 0; i < m-1; ++i) {
pre=pre->next;
}
ListNode* cur=pre->next;
// 反转m到n的这部分链表
ListNode* node=pre;
for (int i = 0; i < n-m+1; ++i) {
ListNode* tmp=cur->next;
cur->next=node;
node=cur;
cur=tmp;
}
// 拼接
pre->next->next=cur;
pre->next=node;
return dummy->next;
}
};



